The sum of these two amounts (less a rounding error) equals the $116,000 total actual cost of all purchases and beginning inventory. When using the weighted average method, divide the cost of goods available for sale by the number of units available for sale, which yields the weighted-average cost per unit. In this calculation, the cost of goods available for sale is the sum of beginning inventory and net purchases. You then use this weighted-average figure to assign a cost to both ending inventory and the cost of goods sold.
Method 2: When the Weights Do Not Add Up to One
The values of each of the above categories can be used as the weight values. Multiply the 15 men who responded “YES” by a weight of 1.667 optimal choice of entity for the qbi deduction (their underrepresentation factor). Divide the 50 women who responded “YES” by a weight of 1.4 (their overrepresentation factor).
Practical Examples
But by using a weighted average, they can calculate the share price paid for each share purchased, not just the absolute price of the portfolio. A common mistake that can happen when working with big datasets is that values and their corresponding weights can get out of sync. Also, mistakes can happen when the goods or weights are added up incorrectly. Using a calculator or spreadsheet can help avoid these kinds of pitfalls. In various fields, from statistics to everyday decision-making, comprehension of basic average concepts is crucial.

Formula for Weighted average
Weighted averages have many applications in many different fields. Investors can use weighted averages to determine the cost basis of their shares as well as the returns on their portfolios. In general, a weighted average will be more useful and more accurate than a simple average, if a little more difficult to calculate.
This total number offers a nuanced view of the surveyed group’s consensus, factoring in the differing significance of each question. This figure with weighted percentage is critical for decision-making regarding investments and funding. The weight that each element carries can be shown by the frequency with which it occurs in the set. The frequency of an element can also be defined as a fraction or percentage of the set.
How to calculate my weighted average if my course work is worth 40%?
- For relatively consistent datasets, this approach works well since it treats all values equally.
- When calculating a weighted average, every term has a corresponding weight.
- ( b ) 10 weighted 25, 12 weighted 30, 16 weighted 20, and 15 weighted at 5.
It also helps in maintaining consistency in measuring the costs incurred by the factories while they procure raw materials. The accountant calculates one cost at the weighted average method and this can be applied to all the costs thus, avoiding a lot of paperwork. On the other hand, this method is very simple and easy compared to other methods just including 3 steps in the process. You add them all together and then divide by how many data points there are.
This is because the total will reflect that some of the bits of data hold more weight or significance than others. Spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets are powerful tools for calculating weighted averages efficiently. These programs offer built-in functions and formulas that make simple process, minimizing the potential for human error. We often use a weighted average to calculate the so-called weighted GPA. To find the weighted average, multiply each number by its respective weights and get the sum. Once you have all the data, you’ll need to know how much each number contributes to your final average.
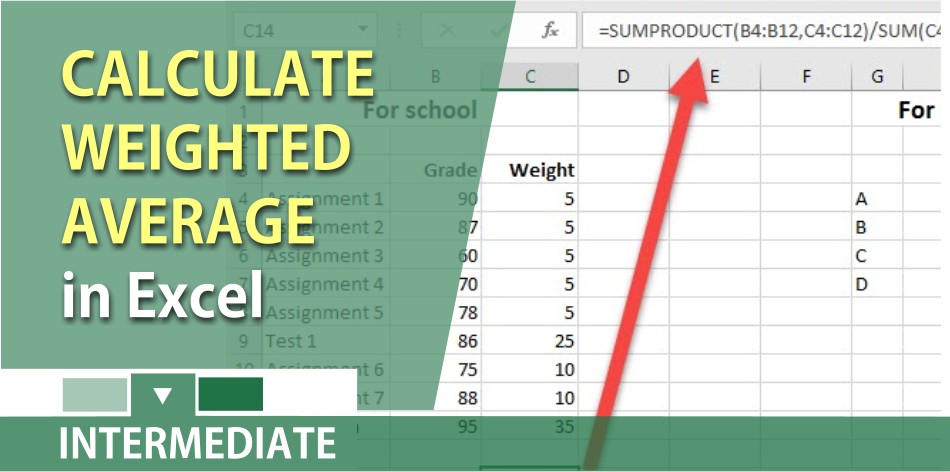
Indeed, the assignments themselves may not all have the same weight because some assignments may be longer or shorter. The weighted average method is mainly utilized to assign the average cost of production to a given product. It is commonly used when items within a business’s inventory are intertwined and it becomes difficult to assign a specific cost to any individual item. Finally, divide the sum of the weighted products by the sum of the weights to find weighted average. Multiply the weight individually by each value and add the results together. This total number is the denominator in the weighted average formula.
For instance, you want to calculate your weighted average in Geometry. Your overall course grades are 88, 92, and 95 for the quizzes, performance tasks, and final exams. Assume that the quizzes are worth 25%, the performance assignments are worth 45%, and the final exam is worth 30% of the total weight. Weighted average can provide a more accurate representation of data when different values within a dataset hold varying degrees of importance.

 Cart is empty
Cart is empty 